目标
使用Gouraud着色算法实现顶点着色
实现
增加Uniform
进行顶点着色之前,需要先给Shader增加两个Uniform变量。其一是法向量变换矩阵,其二是摄像机在世界空间的坐标。
如果你不记得什么是“法向量变换”,可以回顾这篇文章 Java软光栅渲染器-空间变换 中的“法向量变换”部分。
在Renderer中添加一个法向量变换矩阵和一个摄像机位置,并在 render(List
// 法向量变换矩阵
private Matrix3f normalMatrix = new Matrix3f();
// 摄像机位置
private Vector3f cameraPosition = new Vector3f();
/**
* 渲染场景
* @param scene
* @param camera
*/
public void render(List<Geometry> geomList, Camera camera) {
// 根据Camera初始化观察变换矩阵。
viewMatrix.set(camera.getViewMatrix());
projectionMatrix.set(camera.getProjectionMatrix());
viewProjectionMatrix.set(camera.getViewProjectionMatrix());
cameraPosition.set(camera.getLocation());
// TODO 剔除那些不可见的物体
// 遍历场景中的Mesh
for(int i=0; i<geomList.size(); i++) {
Geometry geom = geomList.get(i);
// 根据物体的世界变换,计算MVP等变换矩阵。
worldMatrix.set(geom.getWorldTransform().toTransformMatrix());
viewMatrix.mult(worldMatrix, worldViewMatrix);
viewProjectionMatrix.mult(worldMatrix, worldViewProjectionMatrix);
// 计算法向量变换矩阵
worldMatrix.toRotationMatrix(normalMatrix);
// FIXME 先判断是否为正交矩阵,然后在决定是否要计算Invert、Transpose矩阵。
normalMatrix.invertLocal();
normalMatrix.transposeLocal();
// TODO 使用包围体,剔除不可见物体
// 渲染
render(geom);
}
}
在Shader类中定义同样两个protected成员,并在Renderer中调用shader的set方法设置这些值。
/**
* 渲染单个物体
* @param geometry
*/
protected void render(Geometry geometry) {
// 设置材质
this.material = geometry.getMaterial();
// 设置渲染状态
this.raster.setRenderState(material.getRenderState());
// 设置着色器
Shader shader = material.getShader();
shader.setLights(lights);
raster.setShader(shader);
// 设置全局变量
shader.setWorldMatrix(worldMatrix);
shader.setViewMatrix(viewMatrix);
shader.setProjectionMatrix(projectionMatrix);
shader.setWorldViewMatrix(worldViewMatrix);
shader.setViewProjectionMatrix(viewProjectionMatrix);
shader.setWorldViewProjectionMatrix(worldViewProjectionMatrix);
shader.setNormalMatrix(normalMatrix);//<------ 这里
shader.setCameraPosition(cameraPosition);//<------ 这里
// 遍历所有三角形
for (int i = 0; i < indexes.length; i += 3) {
// ..
}
}
Gouraud着色器
创建GouraudShader类,实现顶点光照计算。
出于性能考虑,我没有实现refract函数来计算光线的反射方向向量,而是使用光线和视线的半途向量(halfVector)来计算反射光的强度。
package net.jmecn.shader;
import net.jmecn.light.AmbientLight;
import net.jmecn.light.DirectionalLight;
import net.jmecn.light.Light;
import net.jmecn.material.Texture;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector3f;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector4f;
import net.jmecn.scene.RasterizationVertex;
import net.jmecn.scene.Vertex;
/**
* Gouraud着色器
* @author yanmaoyuan
*
*/
public class GouraudShader extends Shader {
/// 下列向量,均处于世界空间中
/// 将它们定义为类的成员,避免在光照计算时总是实例化新的对象。
// 顶点坐标
private Vector3f position = new Vector3f();
// 顶点法线
private Vector3f normal = new Vector3f();
// 顶点到光源方向向量
private Vector3f lightVector = new Vector3f();
// 顶点到眼睛方向向量
private Vector3f eyeVector = new Vector3f();
// 光线和眼睛向量之间的半途向量,用于计算高光反射强度。
private Vector3f halfVector = new Vector3f();
// 光照颜色
private Vector4f ambient = new Vector4f();
private Vector4f diffuse = new Vector4f();
private Vector4f specular = new Vector4f();
private Vector3f color = new Vector3f();
/**
* 计算光照
* @param vert
* @param light
*/
private Vector3f lighting(RasterizationVertex vert, Light light) {
color.set(0, 0, 0);
if (light instanceof AmbientLight) {
// 环境光
material.getAmbient().mult(light.getColor(), ambient);
ambient.multLocal(light.getColor().w);
return color.set(ambient.x, ambient.y, ambient.z);
} else if (light instanceof DirectionalLight) {
DirectionalLight dl = (DirectionalLight) light;
// 顶点位置
position.set(vert.position.x, vert.position.y, vert.position.z);
// 顶点法线
normal.set(vert.normal);
// 计算顶点到光源的方向向量
lightVector.set(dl.getDirection().negate());
// 计算顶点到眼睛的方向向量
cameraPosition.subtract(position, eyeVector);
eyeVector.normalizeLocal();
// 计算光线和眼睛向量之间的半途向量,用于计算高光反射强度。
lightVector.add(eyeVector, halfVector);
halfVector.normalizeLocal();
// 计算漫反射强度
float kd = Math.max(normal.dot(lightVector), 0.0f);
// 计算高光强度
float ks = Math.max(normal.dot(halfVector), 0.0f);
ks = (float) Math.pow(ks, material.getShininess());
// 计算漫射光颜色
material.getDiffuse().mult(light.getColor(), diffuse);
diffuse.multLocal(kd);
// 计算高光颜色
material.getSpecular().mult(light.getColor(), specular);
specular.multLocal(ks);
// 计算光最终的颜色
diffuse.addLocal(specular).multLocal(light.getColor().w);
return color.set(diffuse.x, diffuse.y, diffuse.z);
}
return color;
}
@Override
public RasterizationVertex vertexShader(Vertex vertex) {
RasterizationVertex out = copy(vertex);
// 顶点法线
normalMatrix.mult(out.normal, out.normal);
out.normal.normalizeLocal();
// 顶点位置
worldMatrix.mult(out.position, out.position);
out.color.set(0, 0, 0, 1);
// 计算光照
for(int i=0; i < lights.size(); i++) {
Light l = lights.get(i);
Vector3f color = lighting(out, l);
out.color.x += color.x;
out.color.y += color.y;
out.color.z += color.z;
}
// 模型-观察-透视 变换
viewProjectionMatrix.mult(out.position, out.position);
return out;
}
@Override
public boolean fragmentShader(RasterizationVertex frag) {
Texture texture = material.getDiffuseMap();
if (texture != null && frag.hasTexCoord) {
Vector4f texColor = texture.sample2d(frag.texCoord);
frag.color.multLocal(texColor);
}
return true;
}
}
测试用例
写个测试用例,验证一下顶点光照的效果。
package net.jmecn.examples;
import net.jmecn.Application;
import net.jmecn.light.AmbientLight;
import net.jmecn.light.DirectionalLight;
import net.jmecn.material.Material;
import net.jmecn.math.Quaternion;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector3f;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector4f;
import net.jmecn.renderer.Camera;
import net.jmecn.scene.Geometry;
import net.jmecn.scene.shape.Box;
import net.jmecn.shader.GouraudShader;
/**
* 测试Gouraud Shader
* @author yanmaoyuan
*
*/
public class TestGouraudShader extends Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestGouraudShader app = new TestGouraudShader();
app.setResolution(400, 300);
app.setTitle("Test Gouraud Shader");
app.setFrameRate(60);
app.start();
}
// 几何体
private Geometry geometry;
// 旋转
private Quaternion rot = new Quaternion();
@Override
protected void initialize() {
// 初始化摄像机
Camera cam = getCamera();
cam.lookAt(new Vector3f(3, 4, 5), Vector3f.ZERO, Vector3f.UNIT_Y);
// 创建材质
Material material = new Material();
// 设置着色器
material.setShader(new GouraudShader());
// 设置颜色
material.setDiffuse(new Vector4f(1, 1, 1, 1));
// 添加到场景中
geometry = new Geometry(new Box(), material);
rootNode.attachChild(geometry);
// 添加光源
lights.add(new AmbientLight(new Vector4f(0.3f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1f)));
lights.add(new DirectionalLight(new Vector4f(0.7f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1f), new Vector3f(-3, -2, -4).normalizeLocal()));
}
@Override
protected void update(float delta) {
rot.rotateY(delta);
geometry.getLocalTransform().getRotation().multLocal(rot);
}
}
运行程序,效果如下:

有点古怪。。为什么有个面迎着光也是暗的?
检查一下Box类的法线数据,发觉left面和right面的法线方向反了。left面应该指向 (1, 0, 0),而right面应该指向(-1, 0, 0)。
// 顶点法线
float[] normals = {
// back
0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1,
//front
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// left
-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0,
// right
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
// top
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
// bottom
0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0,
};
交换一下这两个面的法线数据。
// 顶点法线
float[] normals = {
// back
0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1,
//front
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// left
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,// <---
// right
-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0,// <---
// top
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
// bottom
0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0,
};
重新运行测试用例。
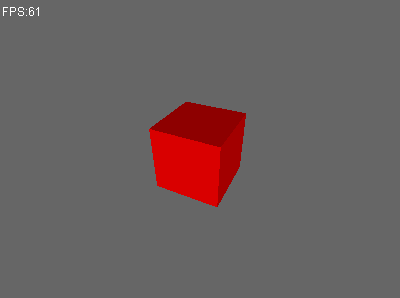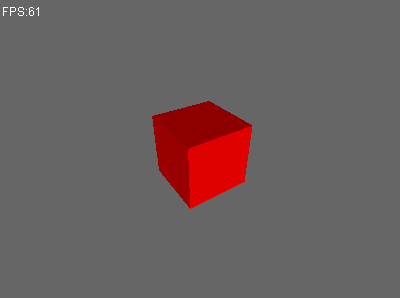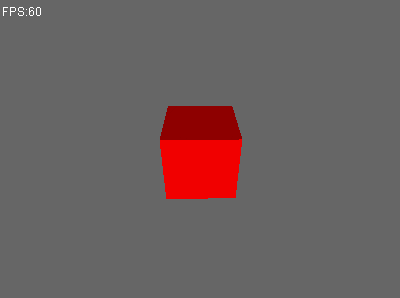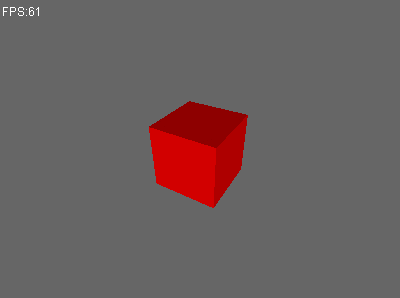
Perfect
总结
目标达成。