目标
- 光栅化3D顶点
- 光栅化3D线段
- 光栅化3D线框三角形
- 光栅化3D实心三角形
- 实现顶点线性插值
实现
本章主要实现SoftwareRaster中对基本形状的光栅化。
计算空间变换矩阵
Renderer中定义了诸多空间变换矩阵,在渲染之前先要把它们初始化。
private Matrix4f worldMatrix = new Matrix4f();
private Matrix4f viewMatrix = new Matrix4f();
private Matrix4f projectionMatrix = new Matrix4f();
private Matrix4f viewProjectionMatrix = new Matrix4f();
private Matrix4f worldViewMatrix = new Matrix4f();
private Matrix4f worldViewProjectionMatrix = new Matrix4f();
private Matrix4f viewportMatrix = new Matrix4f();
视口变换矩阵是在初始化渲染器时就计算好了的。只要窗口大小不变,就不需要重新计算。
/**
* 初始化渲染器
* @param width
* @param height
*/
public Renderer(int width, int height) {
image = new Image(width, height);
raster = new SoftwareRaster(this, image);
// 计算视口变换矩阵
updateViewportMatrix(width, height);
}
/**
* 视口变换矩阵
*/
public void updateViewportMatrix(float width, float height) {
float w = width * 0.5f;
float h = height * 0.5f;
// 把模型移到屏幕中心,并且按屏幕比例放大。
float m00 = w, m01 = 0, m02 = 0, m03 = w;
float m10 = 0, m11 = -h, m12 = 0, m13 = h;
float m20 = 0, m21 = 0, m22 = 1f, m23 = 0;
float m30 = 0, m31 = 0, m32 = 0, m33 = 1;
viewportMatrix.set(m00, m01, m02, m03, m10, m11, m12, m13, m20, m21, m22, m23, m30, m31, m32, m33);
}
/**
* 视口变换矩阵
*/
public void updateViewportMatrix(float xmin, float ymin, float xmax, float ymax, float near, float far) {
// 把模型移到屏幕中心,并且按屏幕比例放大。
float m00 = (xmax - xmin) * 0.5f, m01 = 0, m02 = 0, m03 = (xmax + xmin) * 0.5f;
float m10 = 0, m11 = -(ymax - ymin) * 0.5f, m12 = 0, m13 = (ymax + ymin) * 0.5f;
float m20 = 0, m21 = 0, m22 = (far-near) * 0.5f, m23 = (far + near) * 0.5f;
float m30 = 0, m31 = 0, m32 = 0, m33 = 1f;
viewportMatrix.set(m00, m01, m02, m03, m10, m11, m12, m13, m20, m21, m22, m23, m30, m31, m32, m33);
}
观察变换矩阵 和 投影变换矩阵 在Camera中计算。当Renderer的render方法被调用时,要把camera中的观察变换矩阵、投影变换矩阵等复制到Renderer的对应成员中,便于渲染使用。
世界变换矩阵与Geometry的WorldTransform有关,应当在遍历每一个Geometry时计算。
/**
* 渲染场景
* @param scene
* @param camera
*/
public void render(List<Geometry> geomList, Camera camera) {
// 根据Camera初始化观察变换矩阵。
viewMatrix.set(camera.getViewMatrix());
projectionMatrix.set(camera.getProjectionMatrix());
viewProjectionMatrix.set(camera.getViewProjectionMatrix());
// TODO 剔除那些不可见的物体
// 遍历场景中的Mesh
for(int i=0; i<geomList.size(); i++) {
Geometry geom = geomList.get(i);
// 根据物体的世界变换,计算MVP等变换矩阵。
worldMatrix.set(geom.getWorldTransform().toTransformMatrix());
viewMatrix.mult(worldMatrix, worldViewMatrix);
viewProjectionMatrix.mult(worldMatrix, worldViewProjectionMatrix);
// TODO 使用包围体,剔除不可见物体
// 渲染
render(geom);
}
}
顶点着色阶段
对于Geometry中的每个顶点,要调用vertexShader来对顶点进行空间变换和着色。
/**
* 顶点着色
* @param vert
* @return
*/
protected RasterizationVertex vertexShader(Vertex vert) {
RasterizationVertex out = new RasterizationVertex();
// 顶点位置
out.position.set(vert.position, 1f);
// 顶点法线
if (vert.normal != null) {
out.normal.set(vert.normal);
out.hasNormal = true;
}
// 纹理坐标
if (vert.texCoord != null) {
out.texCoord.set(vert.texCoord);
out.hasTexCoord = true;
}
// 顶点颜色
if (vert.color != null) {
out.color.set(vert.color);
out.hasVertexColor = true;
}
// 顶点着色器
// 模型-观察-透视 变换
worldViewProjectionMatrix.mult(out.position, out.position);
return out;
}
由于现在还没有实现顶点光照,因此vertexShader并不需要做什么特别的事情,只需要把Vertex中的值复制到一个RasterizationVertex对象中,并使用worldViewProjectionMatrix矩阵将顶点位置变换到投影空间。
在render方法中遍历Geometry中的每个三角形,执行vertexShader,然后在观察空间中进行背面剔除。
/**
* 渲染单个物体
* @param geometry
*/
protected void render(Geometry geometry) {
// 设置材质
this.material = geometry.getMaterial();
// 设置渲染状态
this.raster.setRenderState(material.getRenderState());
// 用于保存变换后的向量坐标。
Vector3f a = new Vector3f();
Vector3f b = new Vector3f();
Vector3f c = new Vector3f();
// 提取网格数据
Mesh mesh = geometry.getMesh();
int[] indexes = mesh.getIndexes();
Vertex[] vertexes = mesh.getVertexes();
// 遍历所有三角形
for (int i = 0; i < indexes.length; i += 3) {
Vertex v0 = vertexes[indexes[i]];
Vertex v1 = vertexes[indexes[i+1]];
Vertex v2 = vertexes[indexes[i+2]];
// 执行顶点着色器
RasterizationVertex out0 = vertexShader(v0);
RasterizationVertex out1 = vertexShader(v1);
RasterizationVertex out2 = vertexShader(v2);
// 在观察空间进行背面消隐
worldViewMatrix.mult(v0.position, a);
worldViewMatrix.mult(v1.position, b);
worldViewMatrix.mult(v2.position, c);
if (cullBackFace(a, b, c))
continue;
// TODO 视锥裁剪
raster.rasterizeTriangle(out0, out1, out2);
}
}
然后,就进入了光栅化阶段。
光栅化像素
这个实现很简单,从frag参数中取出color的值,然后转成0~255的整数,保存到Image的components中。components在这里被当做了3D引擎中的帧缓存(FrameBuffer)。
注意:由于frag中的color是使用Vector4f来保存的,要调用clamp方法来把4个通道的值对齐到0.0 ~ 1.0之间,保证颜色的取值有意义。
/**
* 光栅化点
* @param x
* @param y
* @param frag
*/
public void rasterizePixel(int x, int y, RasterizationVertex frag) {
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= width || y >= height) {
return;
}
// 执行片段着色器
fragmentShader(frag);
int index = (x + y * width) * 4;
Vector4f destColor = frag.color;
destColor.x = clamp(destColor.x, 0, 1);
destColor.y = clamp(destColor.y, 0, 1);
destColor.z = clamp(destColor.z, 0, 1);
destColor.w = clamp(destColor.w, 0, 1);
// TODO 深度测试
// TODO Alpha测试
// TODO 混色
// TODO 写入depthBuffer
// 写入frameBuffer
components[index] = (byte)(destColor.x * 0xFF);
components[index + 1] = (byte)(destColor.y * 0xFF);
components[index + 2] = (byte)(destColor.z * 0xFF);
components[index + 3] = (byte)(destColor.w * 0xFF);
}
光栅化3D线段
稍微修改一下ImageRaster中的drawLineBresenham代码,就变成了rasterizeLine方法。
/**
* 光栅化线段,使用Bresenham算法。
* @param v0
* @param v1
*/
public void rasterizeLine(RasterizationVertex v0, RasterizationVertex v1) {
int x = (int) v0.position.x;
int y = (int) v0.position.y;
int w = (int) (v1.position.x - v0.position.x);
int h = (int) (v1.position.y - v0.position.y);
int dx1 = w < 0 ? -1 : (w > 0 ? 1 : 0);
int dy1 = h < 0 ? -1 : (h > 0 ? 1 : 0);
int dx2 = w < 0 ? -1 : (w > 0 ? 1 : 0);
int dy2 = 0;
int fastStep = Math.abs(w);
int slowStep = Math.abs(h);
if (fastStep <= slowStep) {
fastStep = Math.abs(h);
slowStep = Math.abs(w);
dx2 = 0;
dy2 = h < 0 ? -1 : (h > 0 ? 1 : 0);
}
int numerator = fastStep >> 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= fastStep; i++) {
// 线性插值
float t = (y - v0.position.y) / (v1.position.y - v0.position.y);
RasterizationVertex frag = new RasterizationVertex();
frag.interpolateLocal(v0, v1, t);
rasterizePixel(x, y, frag);
numerator += slowStep;
if (numerator >= fastStep) {
numerator -= fastStep;
x += dx1;
y += dy1;
} else {
x += dx2;
y += dy2;
}
// 线性插值
t = (y - v0.position.y) / (v1.position.y - v0.position.y);
frag = new RasterizationVertex();
frag.interpolateLocal(v0, v1, t);
rasterizePixel(x, y, frag);
}
}
对于线段中的每一个像素,使用 t = (y-v0.position.y) / (v1.position.y - v0.position.y)来进行线性插值,可以得到每个像素的颜色。
但是这种算法是有问题的,因为没有考虑线段为水平线的情况。当直线的斜率小于1时,最好使用 t = (x-v0.postion.x) / (v1.position.x - v0.position.x) 来插值。
不过,说实话这个问题影响不大,待会写个测试用例来感受一下。
光栅化线框三角形
这个操作非常简单。先用透视除法把三个顶点变换到投影空间(x/w. y/w. z/w, 1),然后利用视口变换矩阵把顶点位置修正到屏幕空间,最后画三条线段。
/**
* 光栅化三角形
* @param v0
* @param v1
* @param v2
*/
public void rasterizeTriangle(RasterizationVertex v0, RasterizationVertex v1, RasterizationVertex v2) {
// 将顶点变换到投影平面
v0.perspectiveDivide();
v1.perspectiveDivide();
v2.perspectiveDivide();
Matrix4f viewportMatrix = renderer.getViewportMatrix();
// 把顶点位置修正到屏幕空间。
viewportMatrix.mult(v0.position, v0.position);
viewportMatrix.mult(v1.position, v1.position);
viewportMatrix.mult(v2.position, v2.position);
rasterizeLine(v0, v1);
rasterizeLine(v0, v2);
rasterizeLine(v1, v2);
}
测试线框三角形
立方体网格
为了方便后续的测试,我定义了一个立方体网格,它的中心位于模型空间的原点,每个点都有不同的顶点颜色。
代码如下:
package net.jmecn.scene.shape;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector2f;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector3f;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector4f;
import net.jmecn.scene.Mesh;
import net.jmecn.scene.Vertex;
/**
* 立方体网格
* @author yanmaoyuan
*
*/
public class Box extends Mesh {
public Box() {
// 顶点坐标
float[] positions = {
// back
1,-1,-1, -1,-1,-1, 1, 1,-1, -1, 1,-1,
// front
-1,-1, 1, 1,-1, 1, -1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
// left
1,-1, 1, 1,-1,-1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,-1,
// right
-1,-1,-1, -1,-1, 1, -1, 1,-1, -1, 1, 1,
// top
-1, 1,-1, -1, 1, 1, 1, 1,-1, 1, 1, 1,
// bottom
1,-1,-1, 1,-1, 1, -1,-1,-1, -1,-1, 1,
};
// 顶点法线
float[] normals = {
// back
0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1,
//front
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// left
-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0,
// right
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
// top
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
// bottom
0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0, 0,-1, 0,
};
// 纹理坐标
float[] texCoords = {
// back
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
// front
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
// left
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
// right
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
// top
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
// bottom
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
};
// 顶点颜色
float[] colors = {
// back
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,
// front
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
// left
1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,
// right
0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1,
// top
0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
// bottom
1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1,
};
// 顶点索引
this.indexes = new int[]{
// back
0, 1, 3, 0, 3, 2,
// front
4, 5, 7, 4, 7, 6,
// left
8, 9, 11, 8, 11, 10,
// right
12, 13, 15, 12, 15, 14,
// top
16, 17, 19, 16, 19, 18,
// bottom
20, 21, 23, 20, 23, 22,
};
this.vertexes = new Vertex[positions.length];
for(int i = 0; i < indexes.length; i++) {
int index = indexes[i];
vertexes[index] = new Vertex();
vertexes[index].position = new Vector3f( positions[index*3], positions[index*3+1], positions[index*3+2]);
vertexes[index].normal = new Vector3f( normals[index*3], normals[index*3+1], normals[index*3+2]);
vertexes[index].color = new Vector4f( colors[index*4], colors[index*4+1], colors[index*4+2], colors[index*4+3]);
vertexes[index].texCoord = new Vector2f(texCoords[index*2], texCoords[index*2+1]);
}
}
}
测试用例
重构一下以前写的Test3DView代码:
package net.jmecn.examples;
import net.jmecn.Application;
import net.jmecn.material.Material;
import net.jmecn.math.Vector3f;
import net.jmecn.renderer.Camera;
import net.jmecn.scene.Geometry;
import net.jmecn.scene.Mesh;
import net.jmecn.scene.shape.Box;
/**
* 测试3D观察的效果
* @author yanmaoyuan
*
*/
public class Test3DView extends Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test3DView app = new Test3DView();
app.setResolution(400, 300);
app.setTitle("3D View");
app.setFrameRate(60);
app.start();
}
private Geometry geom;
private final static float PI = 3.1415626f;
private final static float _2PI = PI * 2;
private float angle = 0;// 旋转角度
@Override
protected void initialize() {
// 网格
Mesh mesh = new Box();
// 材质
Material material = new Material();
// 添加到场景中
this.geom = new Geometry(mesh, material);
rootNode.attachChild(geom);
// 调整摄像机的位置
Camera cam = getCamera();
cam.lookAt(new Vector3f(3, 4, 8), Vector3f.ZERO, Vector3f.UNIT_Y);
}
@Override
protected void update(float delta) {
// 每秒旋转180°
angle += delta * PI;
// 若已经旋转360°,则减去360°。
if (angle > _2PI) {
angle -= _2PI;
}
// 计算旋转:绕Z轴顺时针方向旋转
geom.getLocalTransform().getRotation().fromAxisAngle(Vector3f.UNIT_Y, -angle);
}
}
运行结果:

还行。
光栅化实心三角形
与ImageRaster一样,先分别光栅化“平底三角形”和“平顶三角形”,用扫描线进行光栅化。然后把任意三角形分成“平顶三角形”和“平底三角形”,分别光栅化。
光栅化扫描线
这个过程跟使用Bresenham算法很像,只是不用关心斜率的问题了。
/**
* 光栅化扫描线
* @param v0
* @param v1
* @param y
*/
public void rasterizeScanline(RasterizationVertex v0, RasterizationVertex v1, int y) {
int x0 = (int) Math.ceil(v0.position.x);
// 按照DirectX和OpenGL的光栅化规则,舍弃右下的顶点。
int x1 = (int) Math.floor(v1.position.x);
for (int x = x0; x <= x1; x++) {
if (x < 0 || x >= width)
continue;
// 线性插值
// FIXME 需要透视校正
float t = (x - v0.position.x) / (v1.position.x - v0.position.x);
RasterizationVertex frag = new RasterizationVertex();
frag.interpolateLocal(v0, v1, t);
rasterizePixel(x, y, frag);
}
}
注意:这个算法的实现是有坑的,需要注意避免重复光栅化相邻三角形的边。一般使用DirectX和OpenGL的规则,舍弃三角形“右下”边上的顶点。
我没有做Edge Equation,只是利用Math.ceil()函数对左顶点靠右取整,用Math.floor()函数对右顶点靠左取整,效果还不错。
光栅化平底三角形
/**
* 画平底实心三角形
* @param v0 上顶点
* @param v1 底边左顶点
* @param v2 底边右顶点
*/
private void fillBottomLineTriangle(RasterizationVertex v0, RasterizationVertex v1, RasterizationVertex v2) {
int y0 = (int) Math.ceil(v0.position.y);
int y2 = (int) Math.ceil(v2.position.y);
for (int y = y0; y <y2; y++) {
if (y >= 0 && y < this.height) {
// 插值生成左右顶点
// FIXME 需要透视校正
float t = (y - v0.position.y) / (v1.position.y - v0.position.y);
RasterizationVertex vl = new RasterizationVertex();
vl.interpolateLocal(v0, v1, t);
RasterizationVertex vr = new RasterizationVertex();
vr.interpolateLocal(v0, v2, t);
//扫描线填充
rasterizeScanline(vl, vr, y);
}
}
}
光栅化平顶三角形
/**
* 画平顶实心三角形
* @param v0 顶边左顶点
* @param v1 顶边右顶点
* @param v2 下顶点
*/
private void fillTopLineTriangle(RasterizationVertex v0, RasterizationVertex v1, RasterizationVertex v2) {
int y0 = (int) Math.ceil(v0.position.y);
int y2 = (int) Math.ceil(v2.position.y);
for (int y = y0; y < y2; y++) {
if (y >= 0 && y < this.height) {
// 插值生成左右顶点
// FIXME 需要透视校正
float t = (y - v0.position.y) / (v2.position.y - v0.position.y);
RasterizationVertex vl = new RasterizationVertex();
vl.interpolateLocal(v0, v2, t);
RasterizationVertex vr = new RasterizationVertex();
vr.interpolateLocal(v1, v2, t);
//扫描线填充
rasterizeScanline(vl, vr, y);
}
}
}
光栅化三角形
激动人心的时刻到了。
/**
* 光栅化三角形
* @param v0
* @param v1
* @param v2
*/
public void rasterizeTriangle(RasterizationVertex v0, RasterizationVertex v1, RasterizationVertex v2) {
// 将顶点变换到投影平面
v0.perspectiveDivide();
v1.perspectiveDivide();
v2.perspectiveDivide();
Matrix4f viewportMatrix = renderer.getViewportMatrix();
// 把顶点位置修正到屏幕空间。
viewportMatrix.mult(v0.position, v0.position);
viewportMatrix.mult(v1.position, v1.position);
viewportMatrix.mult(v2.position, v2.position);
//rasterizeLine(v0, v1);
//rasterizeLine(v0, v2);
//rasterizeLine(v1, v2);
// 按Y坐标把三个顶点从上到下冒泡排序
RasterizationVertex tmp;
if (v0.position.y > v1.position.y) {
tmp = v0;
v0 = v1;
v1 = tmp;
}
if (v1.position.y > v2.position.y) {
tmp = v1;
v1 = v2;
v2 = tmp;
}
if (v0.position.y > v1.position.y) {
tmp = v0;
v0 = v1;
v1 = tmp;
}
float y0 = v0.position.y;
float y1 = v1.position.y;
float y2 = v2.position.y;
if (y0 == y1) {// 平顶
fillTopLineTriangle(v0, v1, v2);
} else if (y1 == y2) {// 平底
fillBottomLineTriangle(v0, v1, v2);
} else {// 分割三角形
// 线性插值
// FIXME 需要透视校正
float t = (y1 - y0) / (y2 - y0);
RasterizationVertex middleVert = new RasterizationVertex();
middleVert.interpolateLocal(v0, v2, t);
if (middleVert.position.x <= v1.position.x) {// 左三角形
// 画平底
fillBottomLineTriangle(v0, middleVert, v1);
// 画平顶
fillTopLineTriangle(middleVert, v1, v2);
} else {// 右三角形
// 画平底
fillBottomLineTriangle(v0, v1, middleVert);
// 画平顶
fillTopLineTriangle(v1, middleVert, v2);
}
}
}
测试效果
重新执行测试用例,看看效果如何。
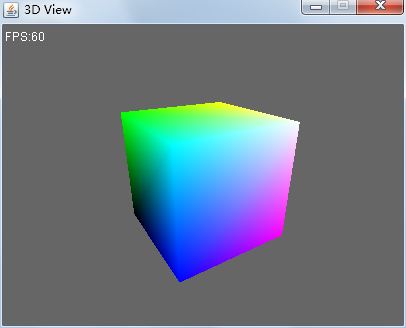
还行。
总结
目标达成。
我在代码中很多地方都注释了 // FIXME 需要透视校正,这些位置是要留给以后改造的。在顶点着色时还看不出来问题,但是到实现纹理采样时问题就大了。
不过这是以后要处理的问题,现在权且标记一下。